Phase Shift π 4 π 4 ( π 4 π 4 to the right) Vertical Shift 0 0 Select a few points to graph Tap for more steps Find the point at x = π 4 x = π 4 Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with π 4 π 4 in the expression f ( π 4) = cos ( ( π 4) − π 4) f ( π 4) = cos ( ( π 4) π 4) Simplify the resultThe appearance of the graph of a function and the properties of that function are very closely related It can be seen from Figure 4 that Figure 4 Even and odd trig functions The cosine is known as an even function, and the sine is known as an odd function Generally speaking, for every value of x in the domain of g Some functions are oddIn the diagram below, the graph of f() = cos x is drawn for xe0%, 3603 3 2 1 O 0 45° 90 135* 180° 225 270° 315 360 1 2 3 31 For which value(s) of x is f decreasing?
H Pre Calc 7 1 7 5 Review Trigonometry
Identify the graph of the trigonometric function f(x) = cos x
Identify the graph of the trigonometric function f(x) = cos x-CalculatorSoup, https//wwwcalculatorsoupcom Online CalculatorsJustification When translating right, the cosine graph must move units When translating to the left, the cosine graph must move units 2 S 2 3S 2S S 0 S 2S 2 3S 2 S f (x) cos(x) g(x) sin(x)) 2 3) cos(2 sin( ) cos(S S x x x This explains the following trigonometric identities The values of k are therefore 2 S k 2 3S k or Only answer C gives




How To Determine The Maximum Of A Sine Graph With Only 2 Known Points Mathematics Stack Exchange
105 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions In this section, we return to our discussion of the circular functions as functions of real numbers and pick up where we left o in Sections1021and1031 As usual, we begin our study with the functions f(t) = cos(t) and g(t) = sin(t) 1051 Graphs of the Cosine and Sine Functions64 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions In this section, we will 1revisit previous sections for important concepts 2graph the basic trig functions (based on the de nitions from prev sections) 3de ne periodicity of a graph and other properties (eg, amplitudes) 4graph transformed trig functionsExample 5 Graph a Damped Cosine Function Sketch a graph of y = x cos x Solution The damping function is y = x and the trigonometric function is y = cos x Start by graphing y = x Then reflect the graph over the xaxis Then graph y = cos x, but the minimums and maximums are at the y = x and y = –x lines Figure 11 y = x cos x
Using this standard notation, the argument x for the trigonometric functions satisfies the relationship x = (180x/ π)°, so that, for example, sin π = sin 180° when we take x = π In this way, the degree symbol can be regarded as a mathematical constant such that 1° = π /180 ≈ Unitcircle definitions32 Sketch the graph of g(x) = sin xThe sin graph passes the xaxis as sin x = 0 there;
Graphing One Period of a Stretched or Compressed Tangent Function We can use what we know about the properties of the tangent function to quickly sketch a graph of any stretched and/or compressed tangent function of the form latexf(x)=A\tan(Bx)/latex We focus on a single period of the function including the origin, because the periodic property enables us to extend the graph3 Identify the xintercepts of g(x)_ At these points, f(x) is undefined There will be vertical asymptotes for these values of x 4 If required, determine what happens to the reciprocal function as x approaches the vertical asymptotes from the left and from the right 5 If required, determine the end behaviour of f(x) Sketching the1) 3 right 2) 3 left 3) 3 up 4) 3 down 11 Given the parent function p(x) cosx, which phrase best describes the transformation used to obtain the graph of g(x) cos(x a) b, if a and b are positive constants?




What Is The Amplitude Of F X Sin X Cos X
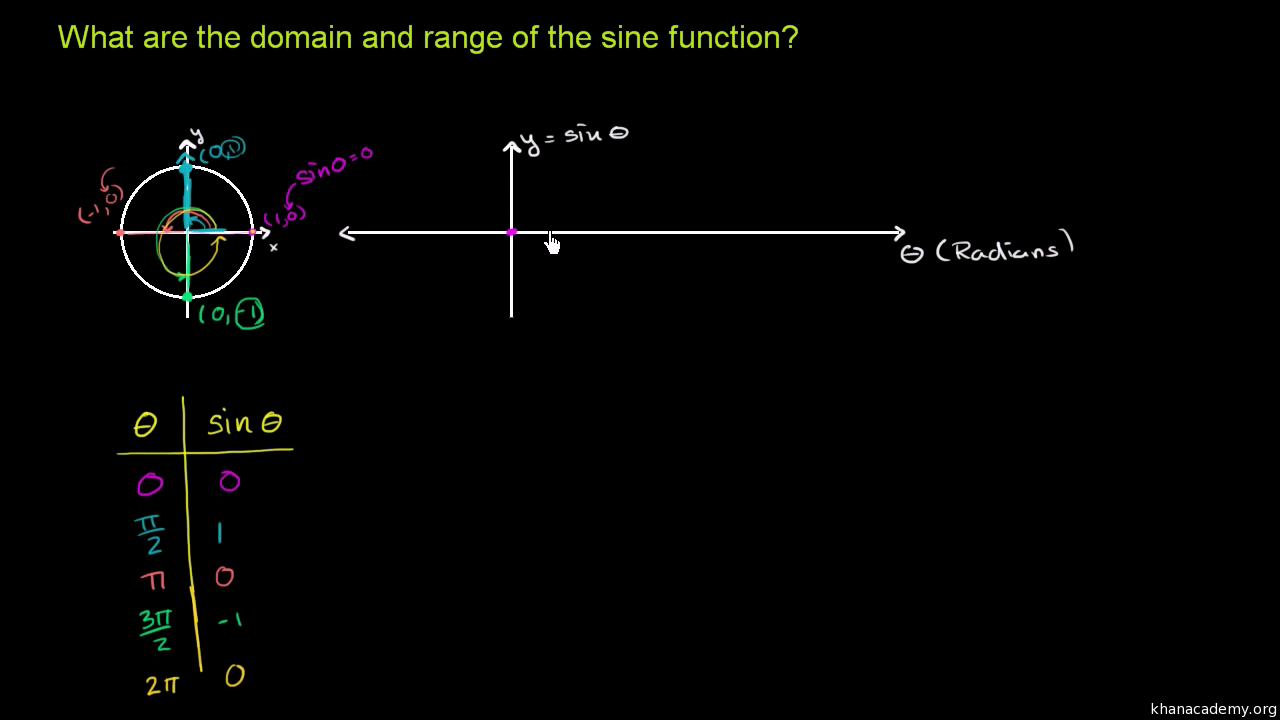



Graph Of Y Sin X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy
To stretch a graph vertically, place a coefficient in front of the function This coefficient is the amplitude of the function For example, the amplitude of y = f (x) = sin (x) is one The amplitude of y = f (x) = 3 sin (x) is three Compare the two graphs below Figure % The sine curve is stretched vertically when multiplied by a coefficientChapter Trigonometric Ratios Upto TransformationsLesson Graphs Of Trigonometric FunctionsFor More Information & Videos visit http//WeTeachAcademycomExcept x ≠nπ, where n exist as any integer value Period 2π Cosecant is an odd function The Graph of cosec(x) function




Is This The Correct Graph Of F X Cos X 45 Askmath




Transformation Of Trigonometric Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
Mar 06, 19 · Below are the graphs of the three trigonometry functions sin x, cos x, and tan x In these trigonometry graphs, xaxis values of the angles are in radians, and on the yaxis, its f(x) is taken, the value of the function at each given angle Sin Graph y = sin x;The graph of y=sin(x) is like a wave that forever oscillates between 1 and 1, in a shape that repeats itself every 2π units Specifically, this means that the domain of sin(x) is all real numbers, and the range is 1,1 See how we find the graph of y=sin(x) using the unitcircle definition of sin(x)The complete equation for the graph shown in this question is \(y = \frac{1}{2}\cos \theta 1\) Therefore \(a = \frac{1}{2}, \text{ and } q= 1\) The graph below shows a trigonometric equation of the following form \(y = a \cos{\theta} q\)




Find Whether F X X Cos X Is One One Identify Whether The Fu




Trigonometric Graphs Amplitude And Periodicity Brilliant Math Science Wiki
Trigonometry Graph f (x)=cos (x) f (x) = cos (x) f ( x) = cos ( x) Use the form acos(bx−c) d a cos ( b x c) d to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift a = 1 a = 1 b = 1 b = 1 c = 0 c = 0 d = 0 d = 0 Find the amplitude a aPurplemath You've already learned the basic trig graphsBut just as you could make the basic quadratic, y = x 2, more complicated, such as y = –(x 5) 2 – 3, so also trig graphs can be made more complicatedWe can transform and translate trig functions, just like you transformed and translated other functions in algebra Let's start with the basic sine function, f (t) = sin(t)Graph Horizontal Dilations of Sinusoidal Functions Describe how the graphs of f (x) = cos x and g (x) = cos are related Then find the period of g (x), and sketch at least one period of both functions on the same coordinate axes Extrema Intercepts Increments Period




Find The Equation Of A Sine Or Cosine Graph Video Lessons Examples And Solutions




For The Function Gx 3 2 Cos 4x 1 Identify The F Gauthmath
The answers to the questions in Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Questions are presented Question 1 Identify the graph of the cosine function f Question 2 Identify the graph of the cotangent function f Question 3 Identify the graph of the cosine function f Question 4 Identify the graph of the cosine function fSine start at 0 and cosine start at 1 How does replacing f(x) with f(x) k, k f(x), f(kx), and f(x k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative) affect the graph?Mar 09, 14 · Find all points on the graph of the function f(x) = 2 cos(x) (cos(x))2 at which the tangent line is horizontal Consider the domain x = 0,2π) I have pi/2 and 3pi/2 for x values But when I plug them I get zero Is this calculus 1




Is This The Correct Graph Of F X Cos X 45 Askmath




Trigonometric Functions From Graphs Mathematics Stack Exchange
Jan 02, 21 · We saw in Section 51 how the graphs of the trigonometric functions repeat every \(2\pi \) radians In this section we will discuss this and other properties of graphs, especially for the sinusoidal functions (sine and cosine) First, recall that the domain of a function \(f(x) \) is the set of all numbers \(x \) for which the function is defined For example, the domain of \(f(x) = \sin\;x \) is the set of all real numbers, whereas the domain of \(f(x) = \tan\;xVisual presentation of changes and behavior of each trigonometric function shows us its graph in the coordinate plane xOy A graph of a function is formed by points P (x, f (x)), where the abscissas x belong to the domain and the calculated values of the function f (x) as the ordinates, which are the corresponding values from the rangeYou can use the graphing calculator to graph trig functions, as follows Graphing Trig Functions Instructions Screens Push " Y= " and enter the trig equation in Y1 using the sin, cos, or tan buttons (followed by X,T,Ɵ,n ) (You don't need to close the parentheses after the , unless you're doing more calculations)




1 Trigonometry 1 0 Introduction 1 1 Sum And Product Formulae Objectives Pdf Free Download




In This Section We Will Continue To Work With The Chegg Com
Trigonometry questions and answers;Find the period of the graph y = sin 2x and sketch the graph of y = sin 2x for 0 ≤ 2x ≤ π Solution Since B = 2, the period is P = 2π/B = 2π/2 = π Phase Shift of Trigonometric Functions The general form for the equation of the sine trigonometric function is y = A sin B(x C)Dec 14, 19 · To plot a trigonometric function (say sine), firstly, assume values for θ, then solve for sin(θ) You can do this by inputting in using a scientific calculator Before the existence of these calculators, people had to use trigonometric tables to get the ratio value After solving, plot the graph with θ on the xaxis while the ratio value on the yaxis




Clp Notes 100 Pages 251 300 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Intersection Points Of Y Sin X And Y Cos X Video Khan Academy
F(x) = cos x 1 2 So now we say that our function f(x) = cosx has domain 0 ≤ x ≤ 180 and that it has an inverse, f−1(x) = cos−1 x This inverse function is also written as arccosx So, if the angle x lies in the range 0 ≤ x ≤ 180 and cosx = 1 2, we say x = cos−1(1 2) Key PointDec 23, 19 · 10 The focus of this answer is on the question of loops vs pgfplots Loops in pgfplots can be slightly more tricky than in plain Ti k Z This is because of the way pgfplots surveys and finally "does" the contents of the axis A detailed discussion can be found in section 81 Utility Commands of the manual v116Cosecant Graphs ƒ ( π) scale 2 π to 2 π radians Graphs of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Cite this content, page or calculator as Furey, Edward " Trigonometric Function Graphs F (x) ";




A Cos X B Sin X R Cos X A Pdf Free Download



Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii
The function f (x) = tanx has a period of π Solving or graphing a trig function must cover a whole period The range depends on each specific trig function For example, the inverse function f (x) = 1 cosx = secx has as period 2πFor a trig function, the range is called "Period" For example, the function f (x) = cosx has a period of 2π;Trigonometric Functions In this section we will explore the graphs of the six trigonometric functions, beginning with the graph of the cosine function Graphing y = cos x To sketch a graph of y = cos x we can make a table of values that we can compute exactly We can plot these points and sketch a smooth curve going through them
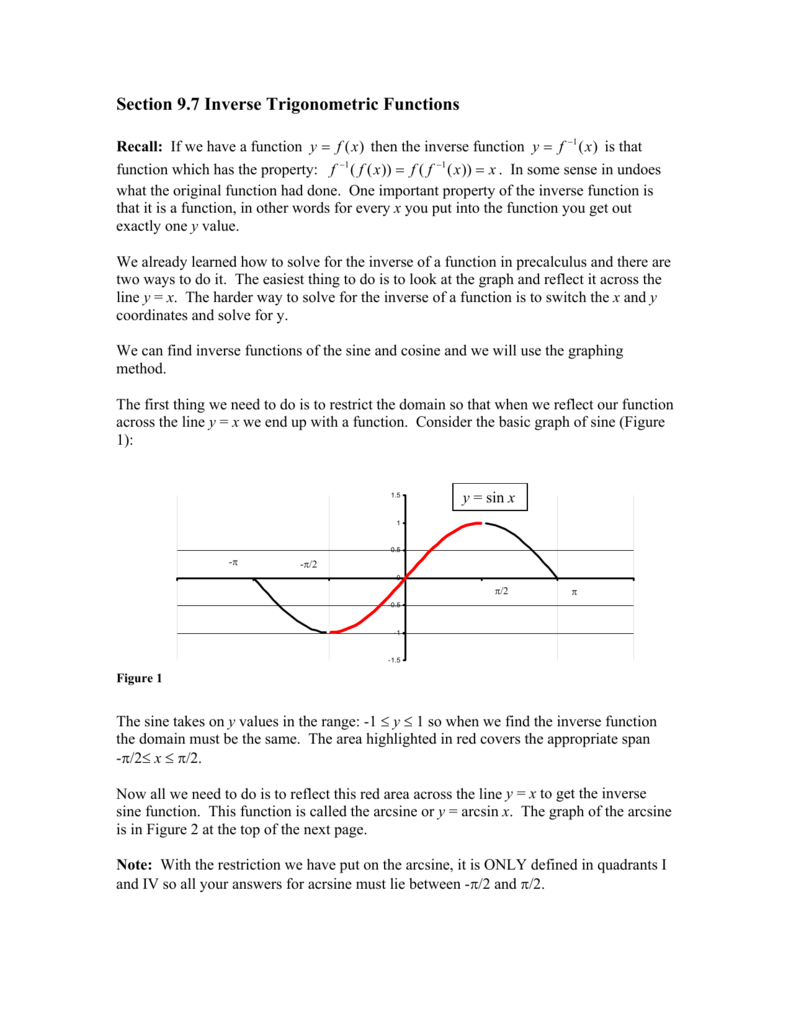



Section 9 7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions




Properties Of Trigonometric Inverse Functions Identities Videos Examples
Domain and Range For Cosecant Function y=f(x)=cosec(x) Range (∞,1 ∪ 1,∞) Domain Defined for all x real values;Graph the trigonometric function f(x) = 2 cos(05x) 2 sin(05x) (a) What does the graph initially look like?How can a trigonometric function be chosen to model periodic phenomena with specified amplitude, frequency, and midline?




Examples With Trigonometric Functions Even Odd Or Neither Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
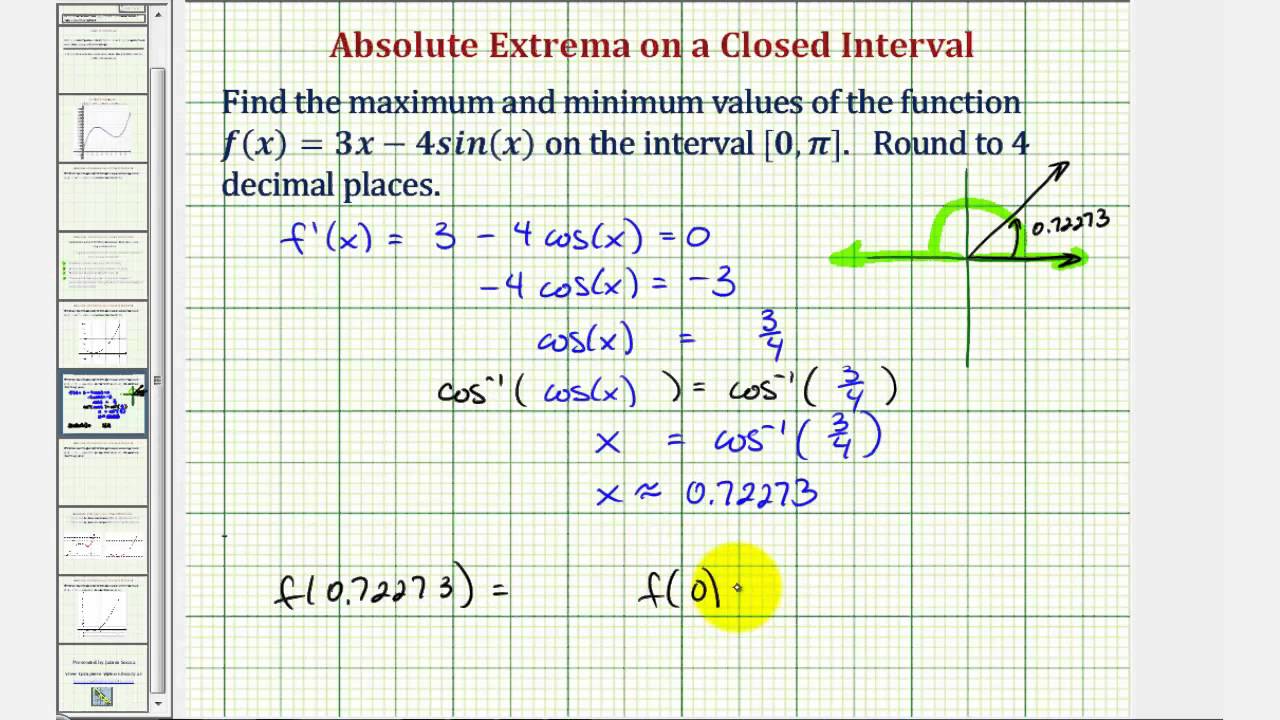



Ex Absolute Extrema Of A Trigonometric Function On A Closed Interval Youtube
Nov 24, 17 · We can use this fact to sketch or draw the graphs of trigonometric functions To draw the graph of a trigonometric function , follow these steps 1 Find the period of the function 2 Choose a suitable interval for the graph Generally, 0, 2π is a good interval for sin x and cos x, (0, π) is good for cot x and (π/2, π/2) is good for tan xThere are two ways to prepare for graphing the basic sine and cosine functions in the form y = sin x and y = cos x evaluating the function and using the unit circle To evaluate the basic sine function, set up a table of values using the intervals 0π, π 2, 3π 2, and 2π for x and calculating the corresponding y value f(x) or y = sin x f(xThe roots or zeros of y = sin x is at the multiples of π;
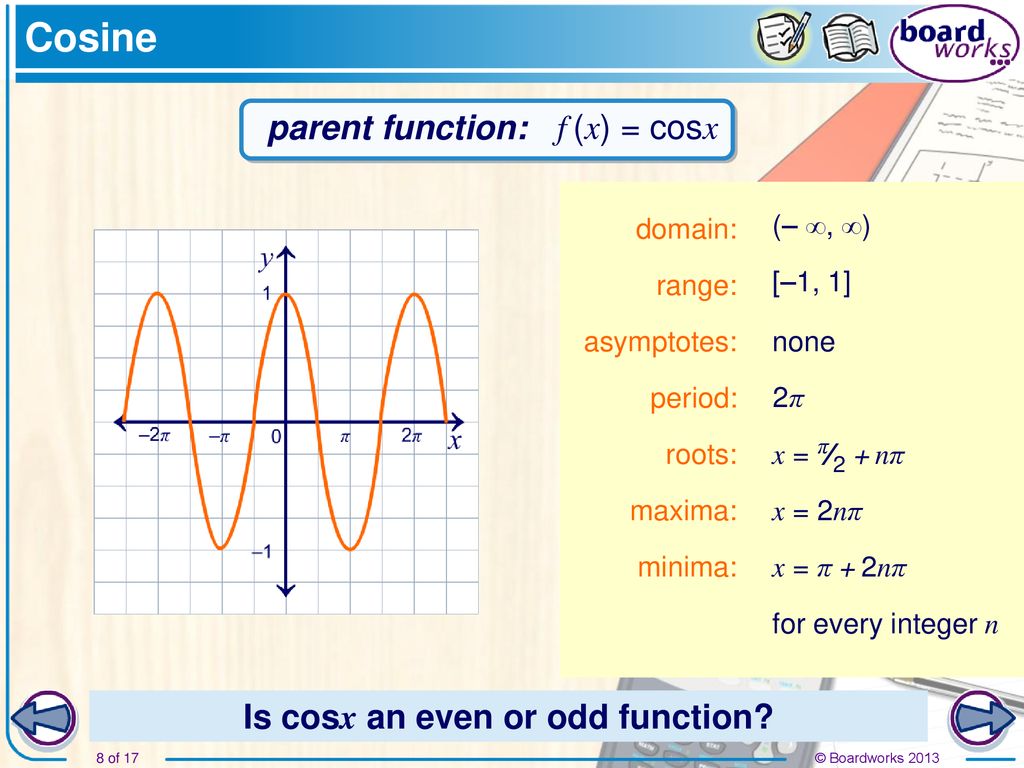



Trigonometric Functions Ppt Download



Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii
10 Relative to the graph of y 3sinx, what is the shift of the graph of y 3sinx 3 Ê Ë ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ˆ ¯ ˜˜ ˜˜ ˜˜?The graph of the cosine function looks like this The domain of the function y = cos ( x ) is all real numbers (cosine is defined for any angle measure), the range is − 1 ≤ y ≤ 1 The graph of the tangent function looks like thisFeb 04, 19 · Trigonometric functions are also known as a Circular Functions can be simply defined as the functions of an angle of a triangle It means that the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle are given by these trig functions The basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant




1 Trigonometry 1 0 Introduction 1 1 Sum And Product Formulae Objectives Pdf Free Download




Is The Function F X Cos X Even Odd Or Neither Socratic
Symmetry since cos(–x) = cos(x) then cos (x) is an even function and its graph is symmetric with respect to the y axis • Intervals of increase/decrease over one period and from 0 to 2π, cos (x) is decreasing on (0 , π) increasing on (π , 2π)Now vary d and note the effect on the graph offSep 23, 18 · Graph the function by determining the key features of the curve represented by y = x 2 \ cos \ x, 0 \leq x \leq 2 \pi Identify any local and
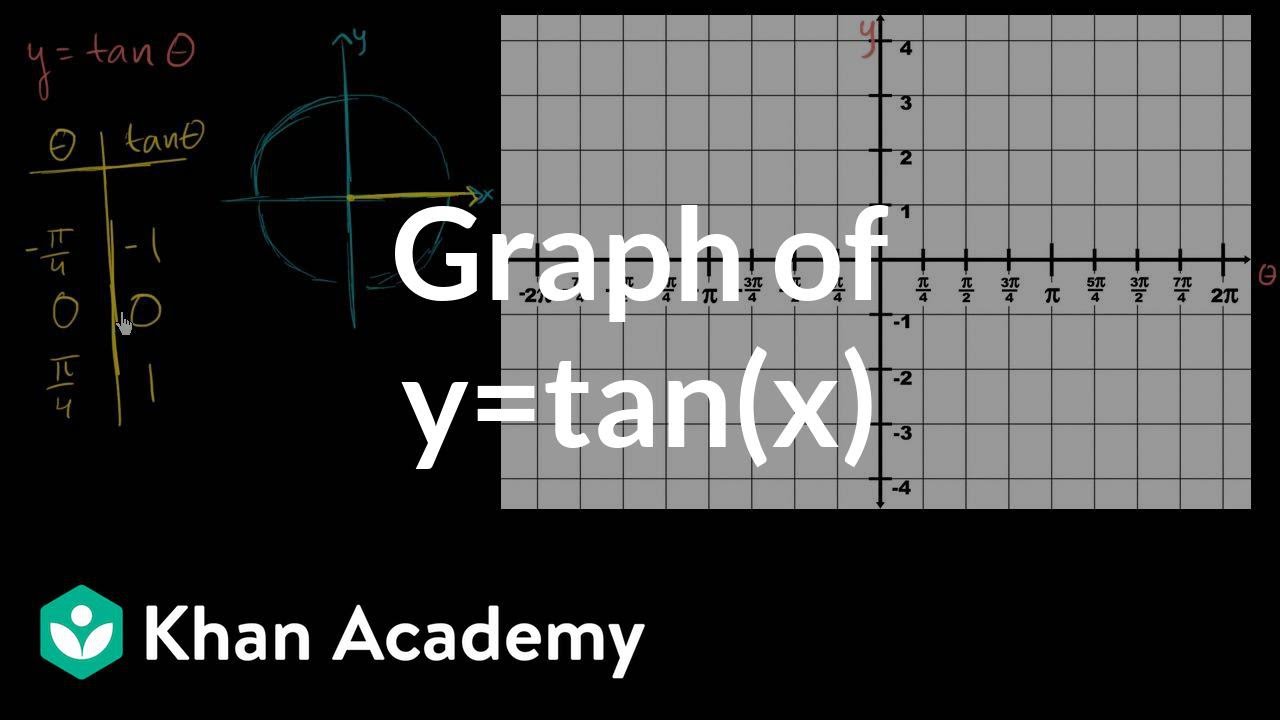



Graph Of Y Tan X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Derivative Of Cos X From First Principles Youtube
Dec 02, 19 · b Composite Trigonometric Graphs Product of Functions The following examples show composite trigonometric graphs where we are taking the product of two functions Example 6 Graph the function y = x sin x In this example, we are multiplying the sine of each xvalue by the xvalue So for example, if `x = 2`, the yvalue will be `y = 2 sinUsing the properties of symmetry above, we can show that sine and cosine are special types of functions A function f (x) f(x) f (x) is an even function if and only if for all real values of x x x, f (− x) = f (x) f(x)=f(x) f (− x) = f (x) In other words, the graph is symmetric about y y yaxis1) right a units



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




Find The Values Of A B And C From Sin Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange
Period of the sine functionGraphs of trigonometric functions The graph of the cosine function f ( x) = cos x To draw the graph of the cosine function divide the unit circle and x axis of a Cartesian coordinate system the same way as when drawing the sine function The abscissas of the ending points of arcs x, of the unit circle, are now the ordinates of theJan 02, 21 · Definition Trigonometric functions Let P = (x, y) be a point on the unit circle centered at the origin O Let θ be an angle with an initial side along the positive x axis and a terminal side given by the line segment OP The trigonometric functions are then defined as sinθ = y cscθ = 1 y cosθ = x secθ = 1 x




How To Determine The Maximum Of A Sine Graph With Only 2 Known Points Mathematics Stack Exchange




H Pre Calc 7 1 7 5 Review Trigonometry




Answered 1 For The Function F X X 1 E A Bartleby




Exam Trigo Adv Algebra 4th Final Trigonometric Functions Sine



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions
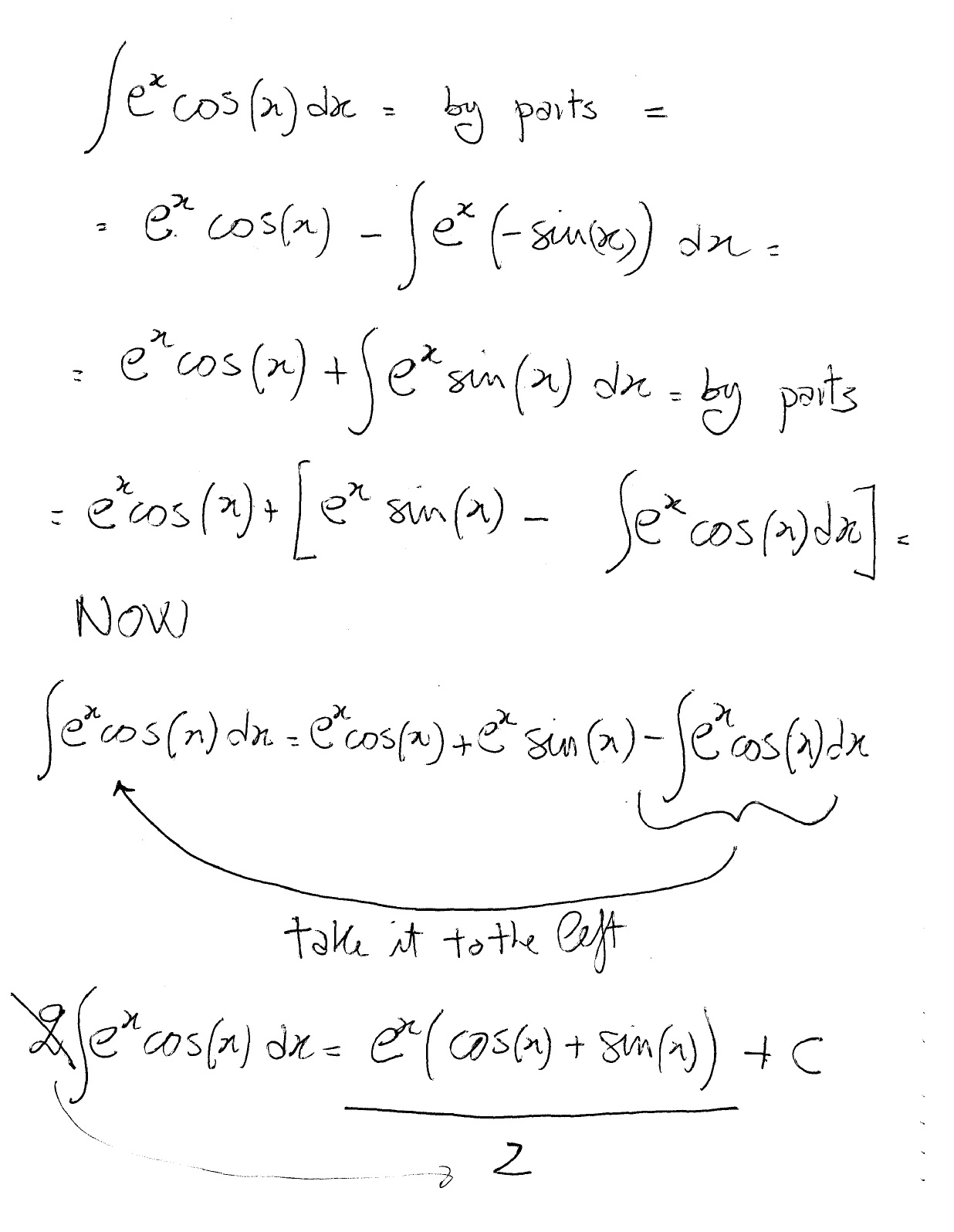



How Do You Find The Integral Of E X Cosx Dx Socratic




Question Video Finding The Maximum And Minimum Values Of A Function Involving Trigonometric Functions Nagwa
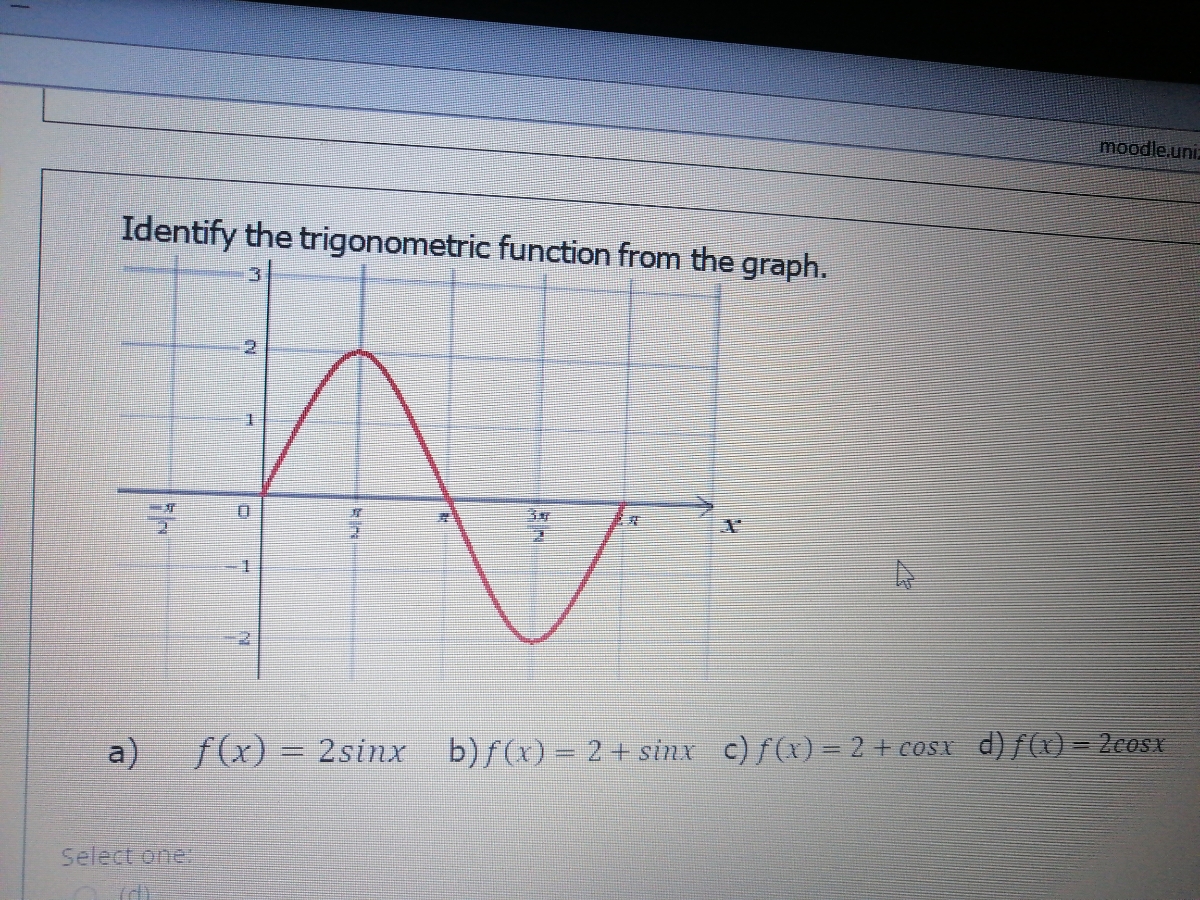



Answered Identify The Trigonometric Function Bartleby




5 2 Properties Of Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Mathematics Libretexts
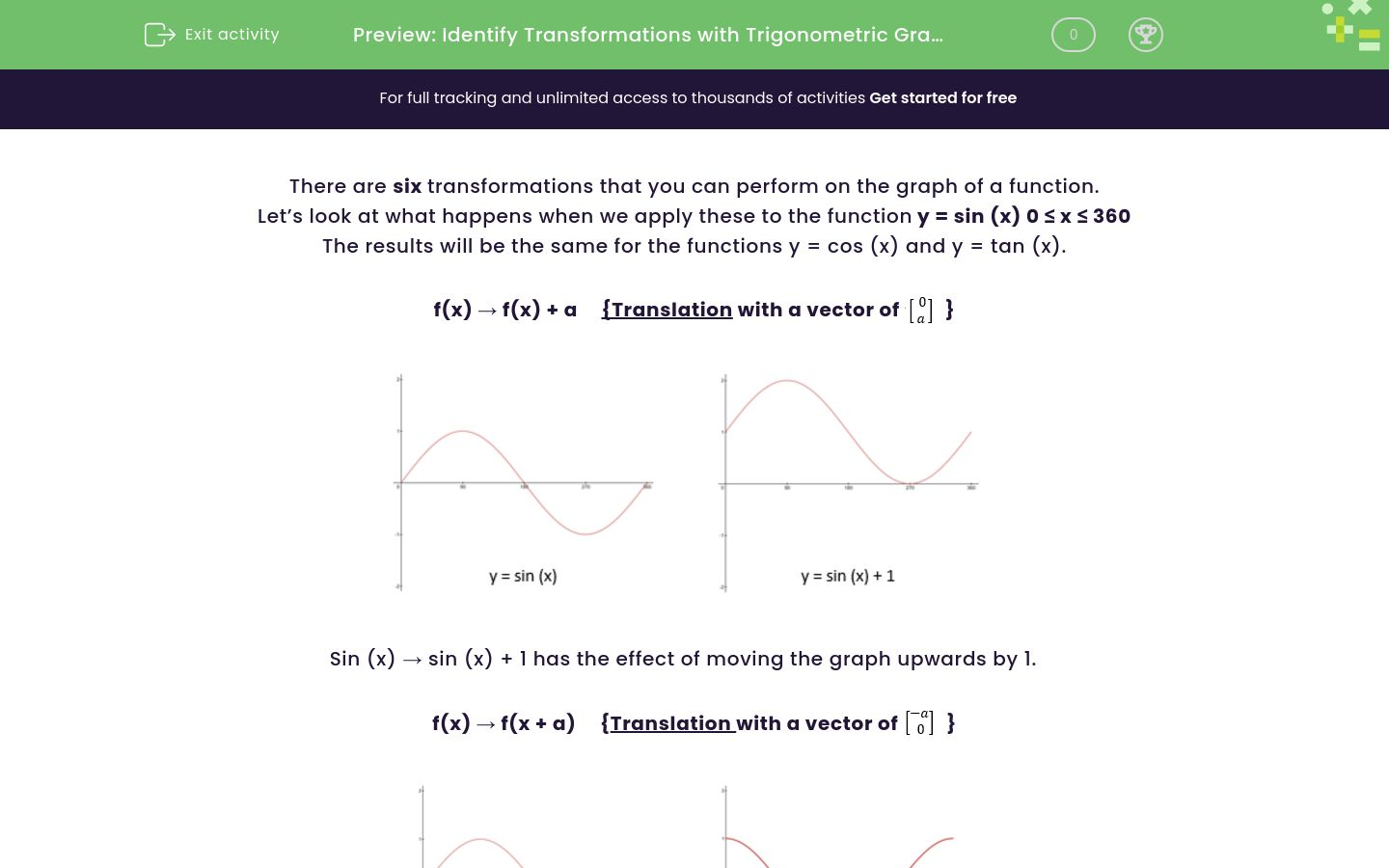



Identify Transformations With Trigonometric Graphs Worksheet Edplace




Derivative Rules For Trigonometric Functions




Trigonometric Functions Wikipedia




Limits Involving Trigonometric Functions Docx Document




Finding Amplitude And Period Of Sine Functions Expii
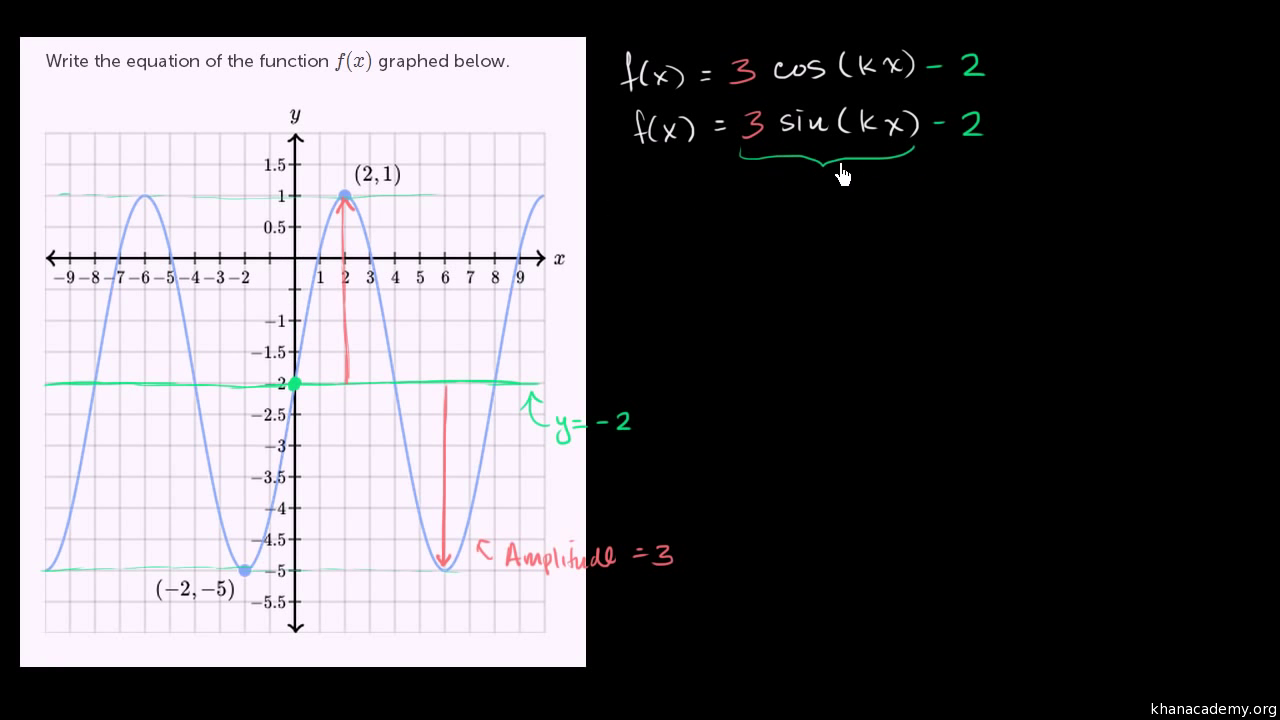



Trigonometric Functions Algebra All Content Math Khan Academy
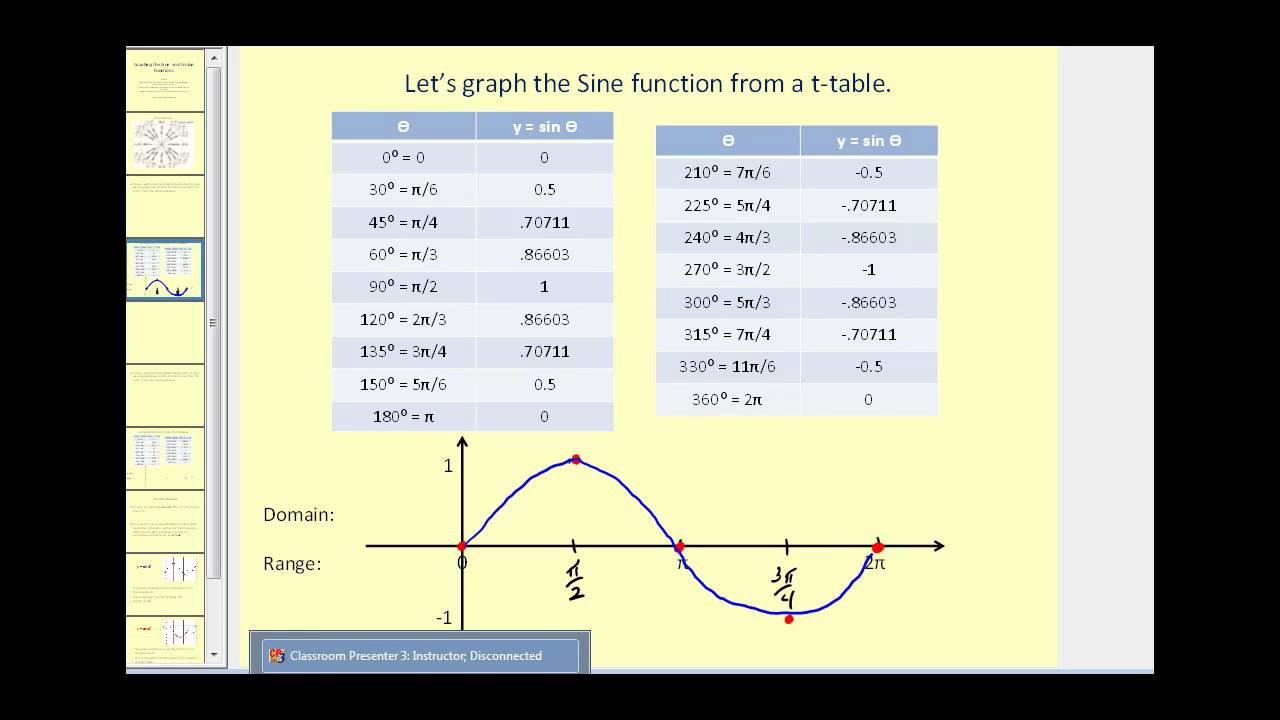



Sine Cosine Tangent Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
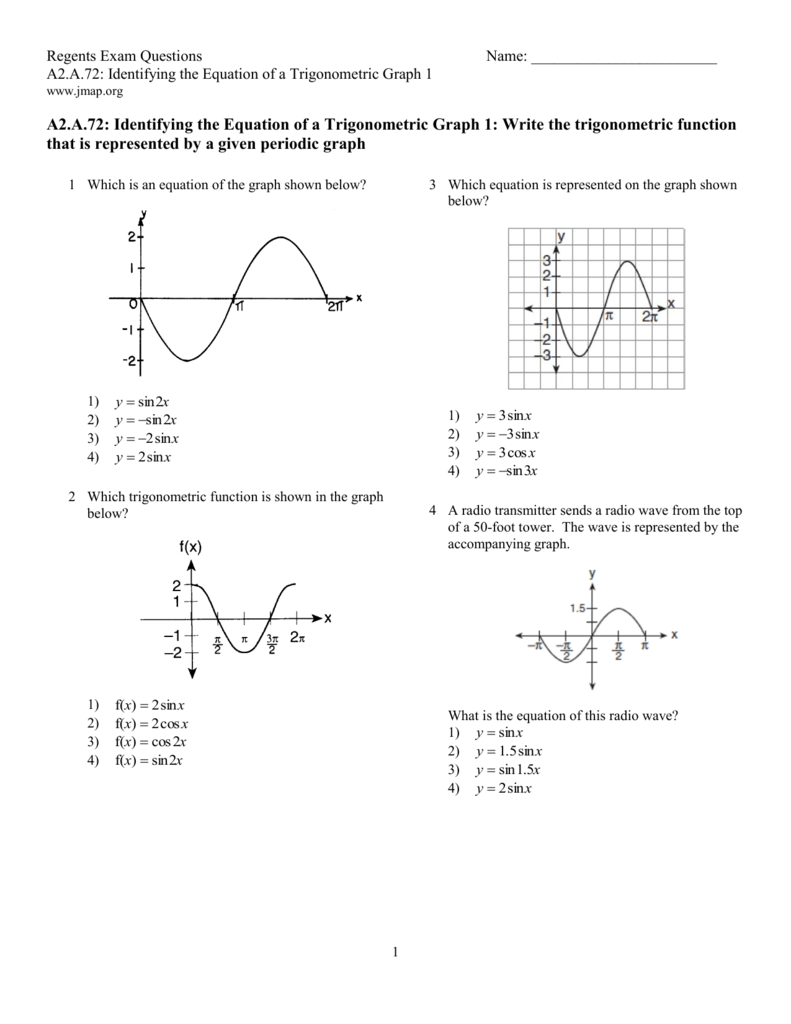



A 72 Identifying The Equation Of A Trigonometric Graph 1 Write



What Is The Fourier Series Of F X Cos X If 0 X P Using Trigonometric Formula Quora




Derivatives Of Sin X And Cos X Video Khan Academy



Nearpod




Notes On Topics Of Algebra Notes
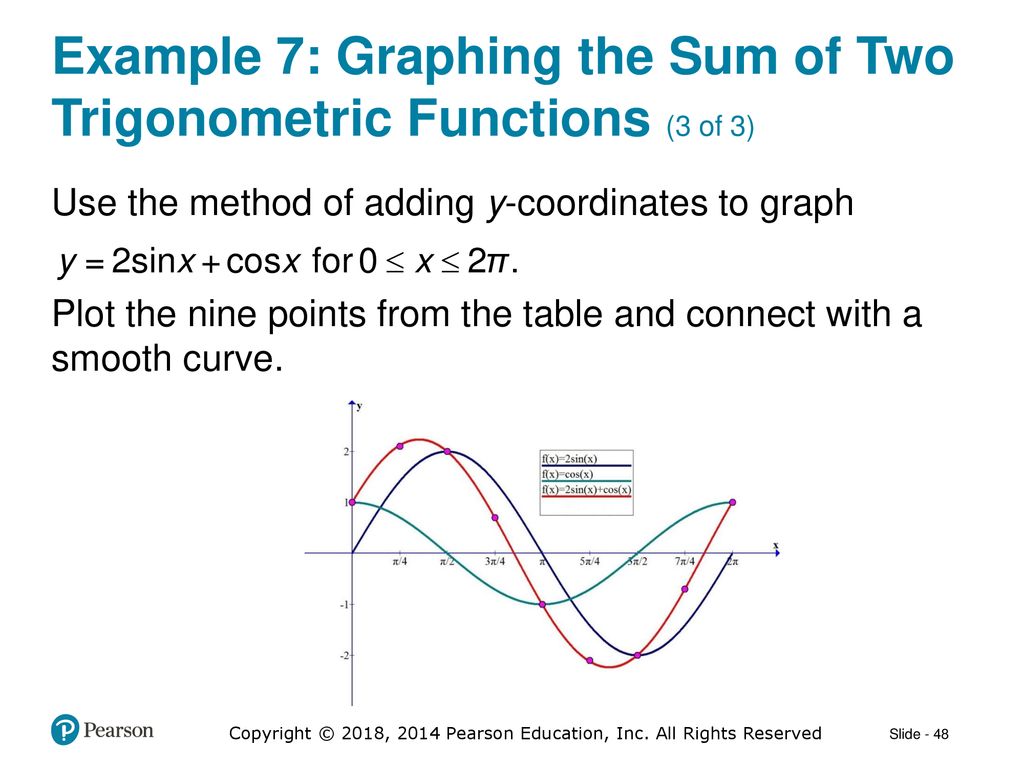



2 1 Graphs Of Sine And Cosine Functions Ppt Download




Range Of The Function F X Cos 1 X Where Is Fra




Answered 3 3 Increasing And Decreasing Functions Bartleby




Interval Of Increase Decrease For Cosine Function Youtube




2 3 Basic Trigonometric Graphs Mathematics Libretexts




Translating Sine And Cosine Functions Ck 12 Foundation
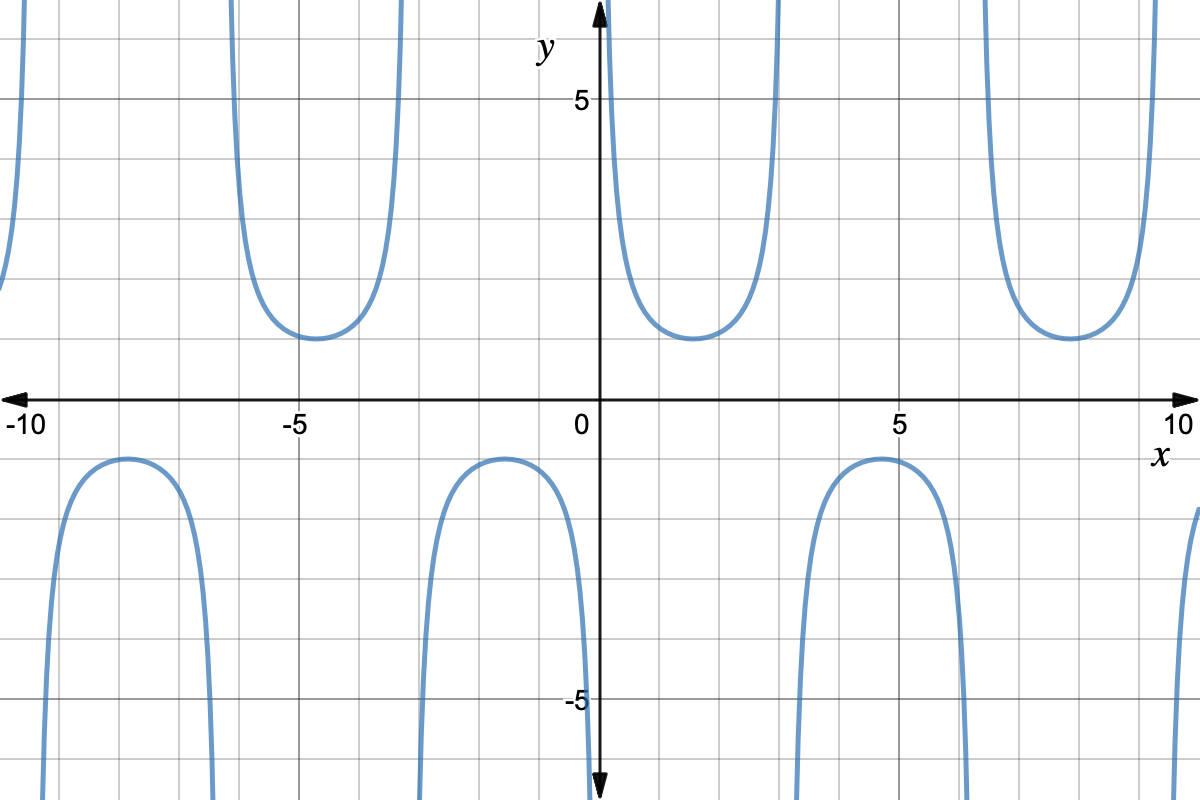



Trigonometry Reciprocal Identities Expii
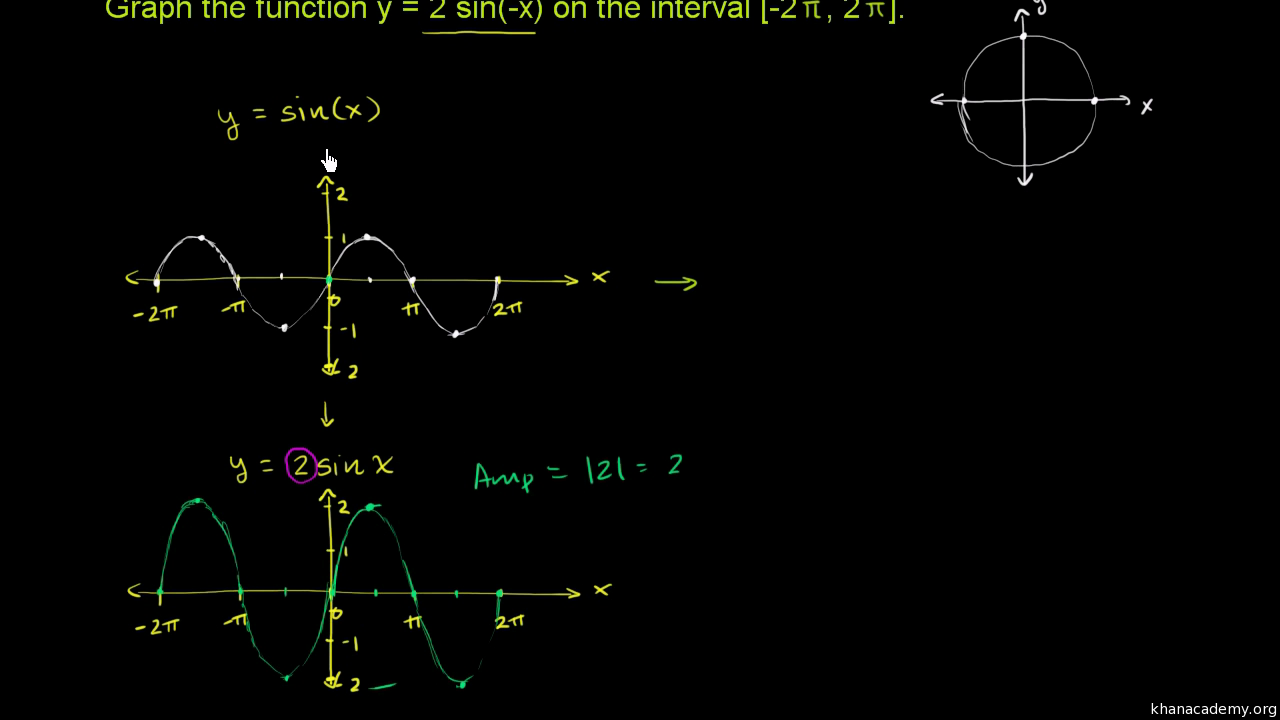



Transforming Sinusoidal Graphs Vertical Stretch Horizontal Reflection Video Khan Academy




How To Find The Absolute Extrema Of F X Sinx Cosx On 0 Pi Youtube




Answered F X X Cos X 1 X Cos X 1 Bartleby
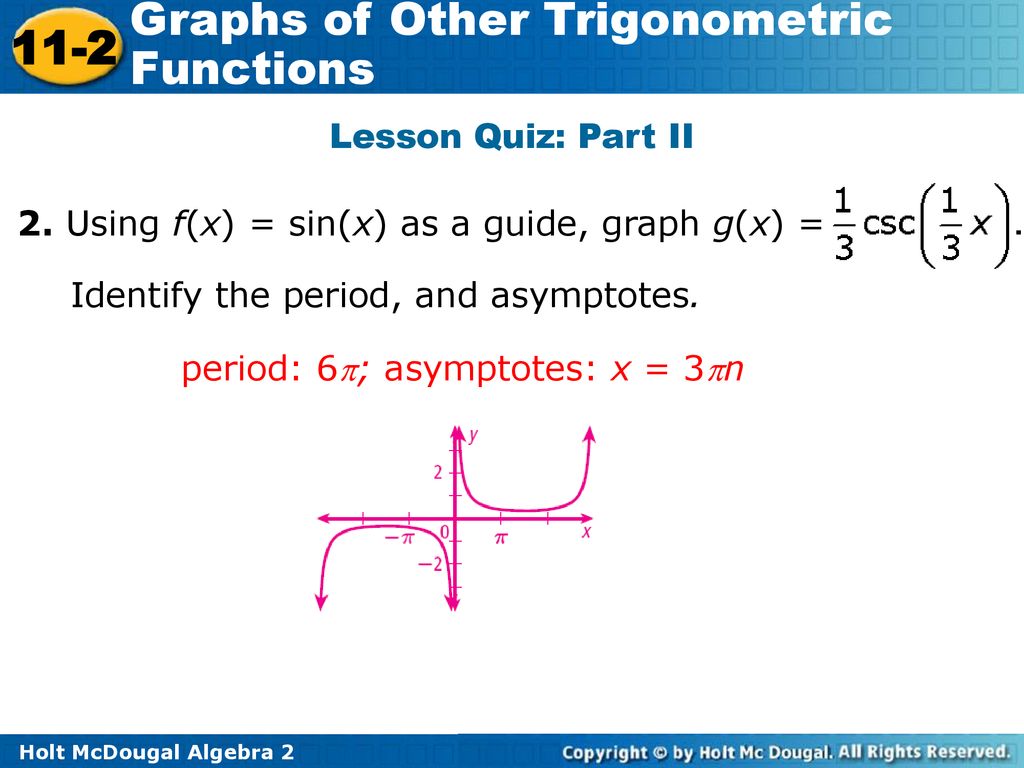



Graphs Of Other Trigonometric Functions Ppt Download
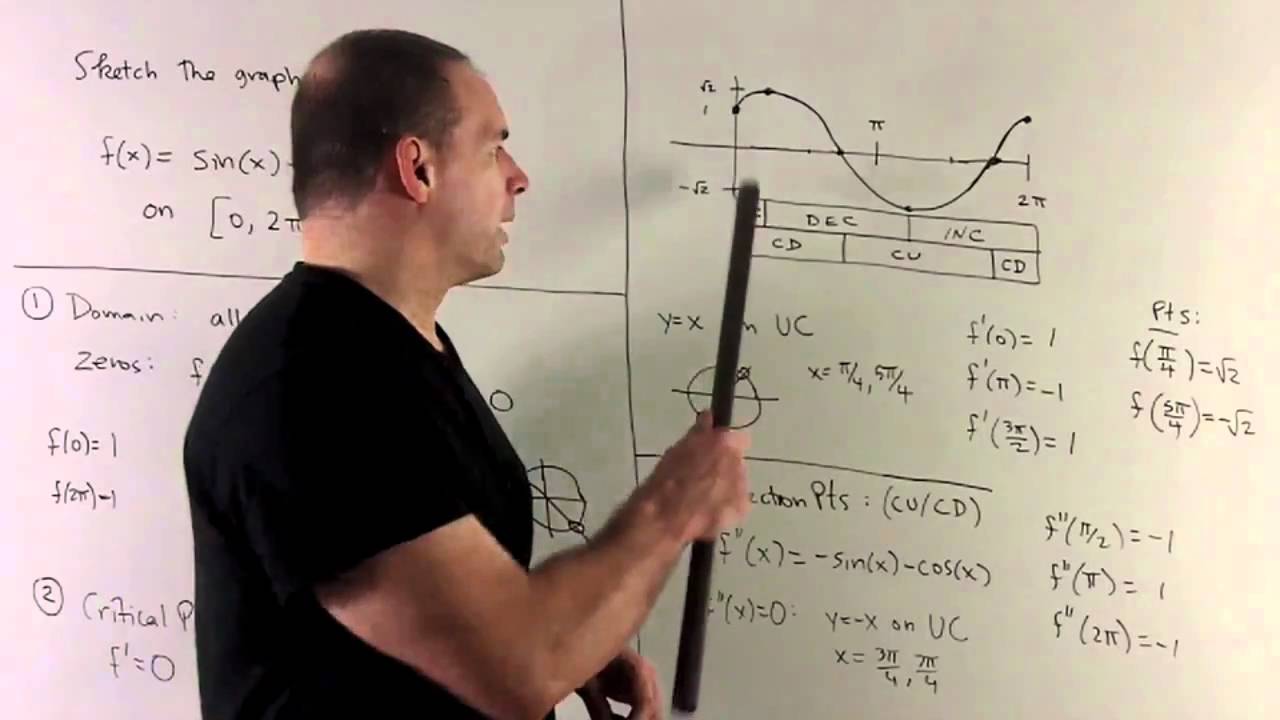



Graph Of F X Sin X Cos X Youtube




Teaching Transformations Of Trigonometric Functions With Technology




Finding Extrema With Trig Functions Youtube
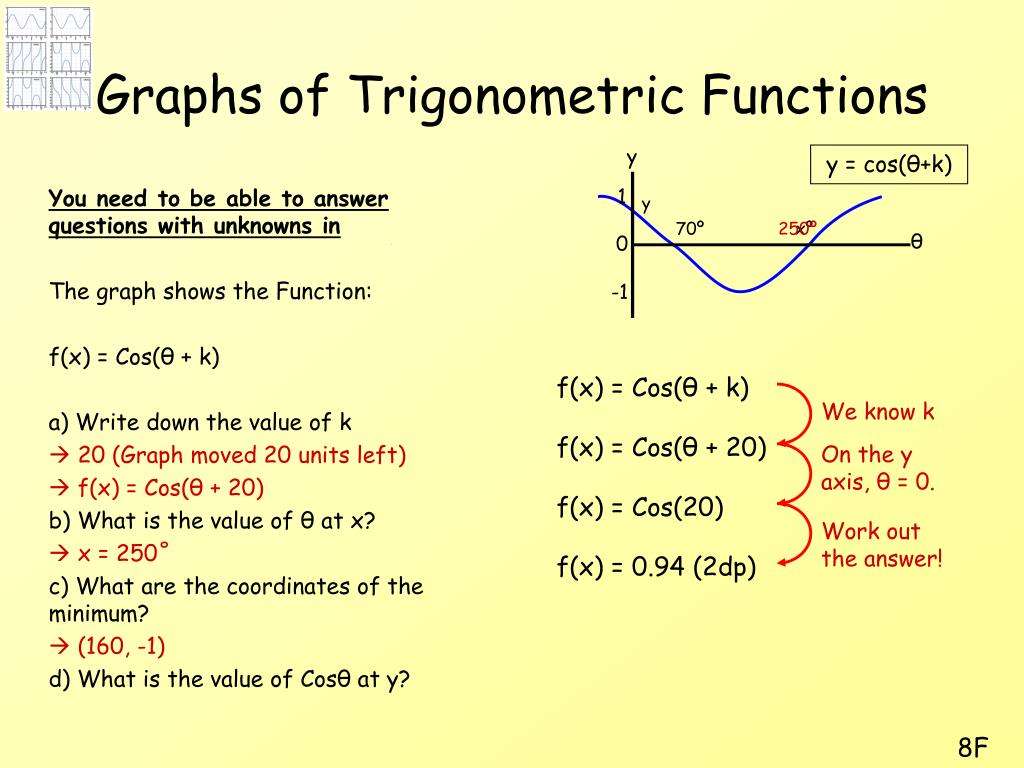



Ppt Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




What Is The Range Of Sin And Cos
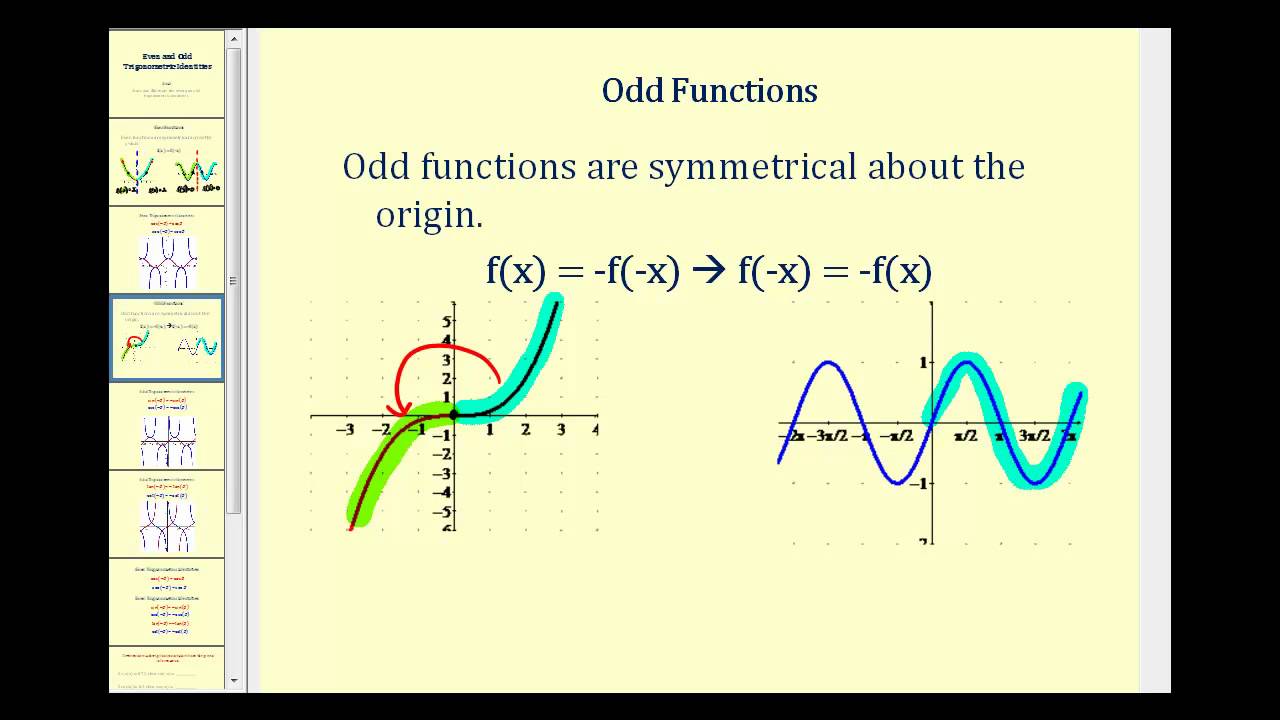



The Other Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii
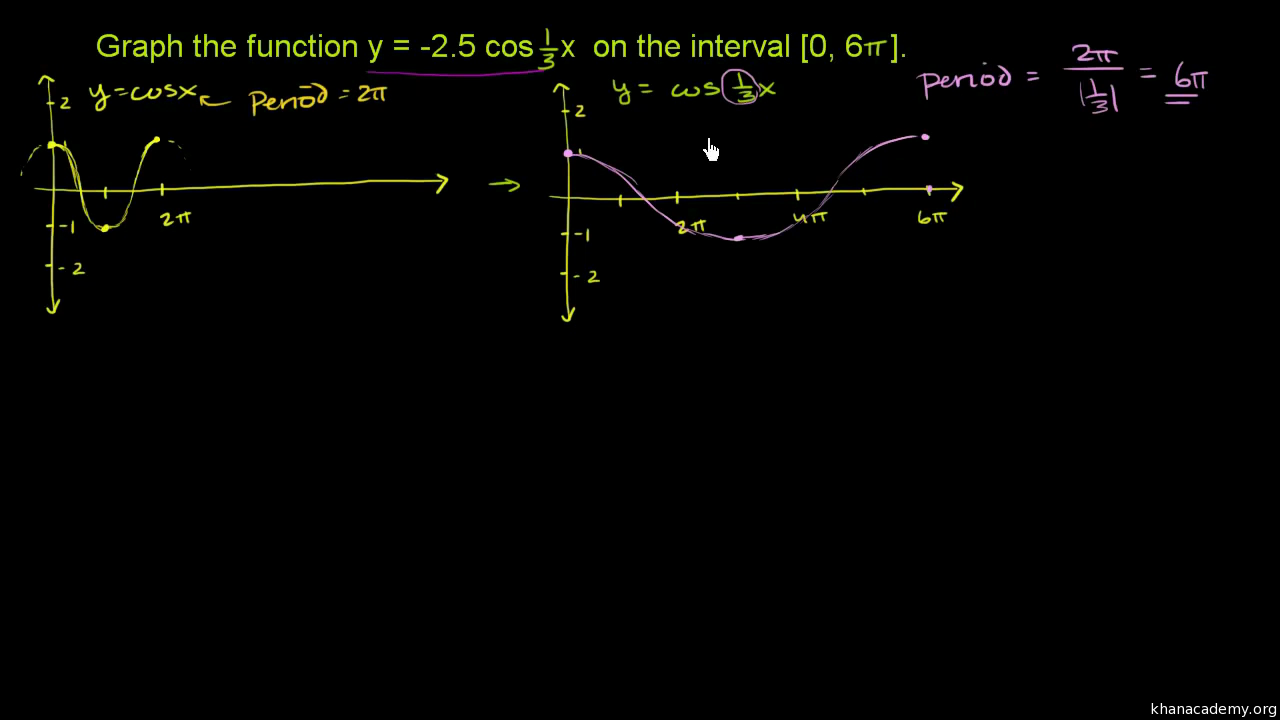



Transforming Sinusoidal Graphs Vertical Horizontal Stretches Video Khan Academy




2 3 Basic Trigonometric Graphs Mathematics Libretexts




Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii
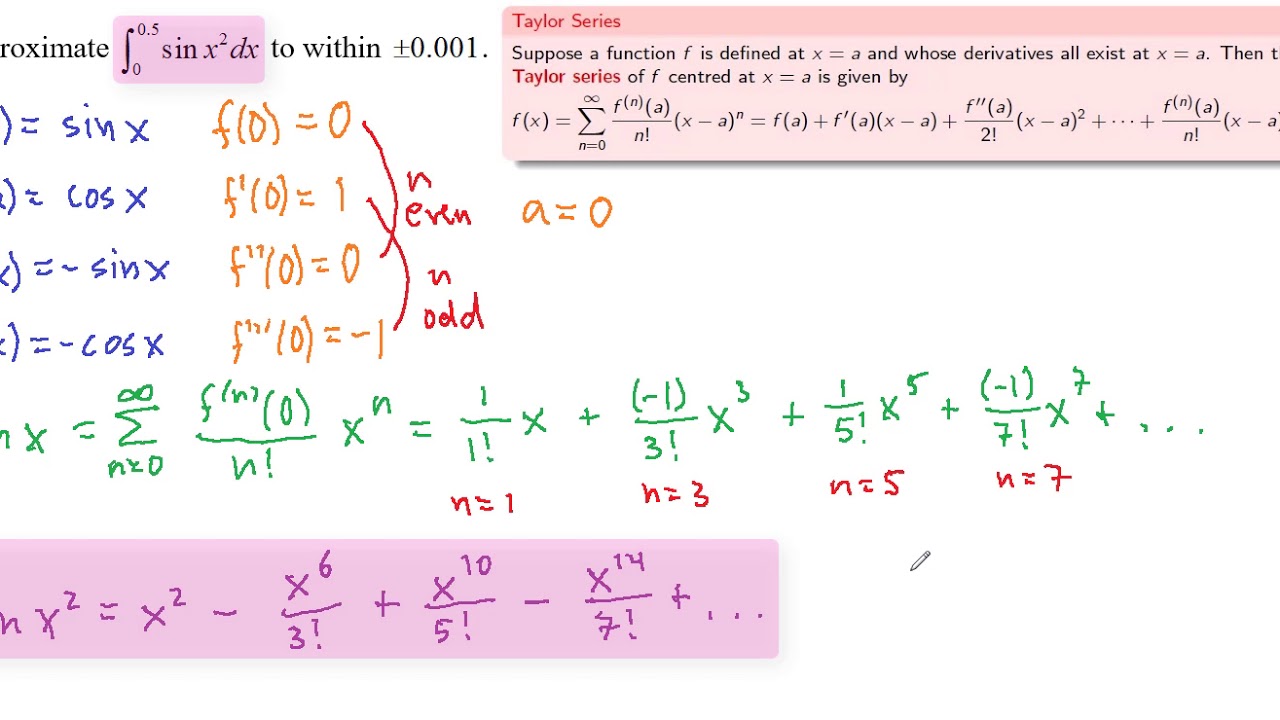



Power Series And Polynomial Approximation




Reflections Of Trig Graphs Examsolutions
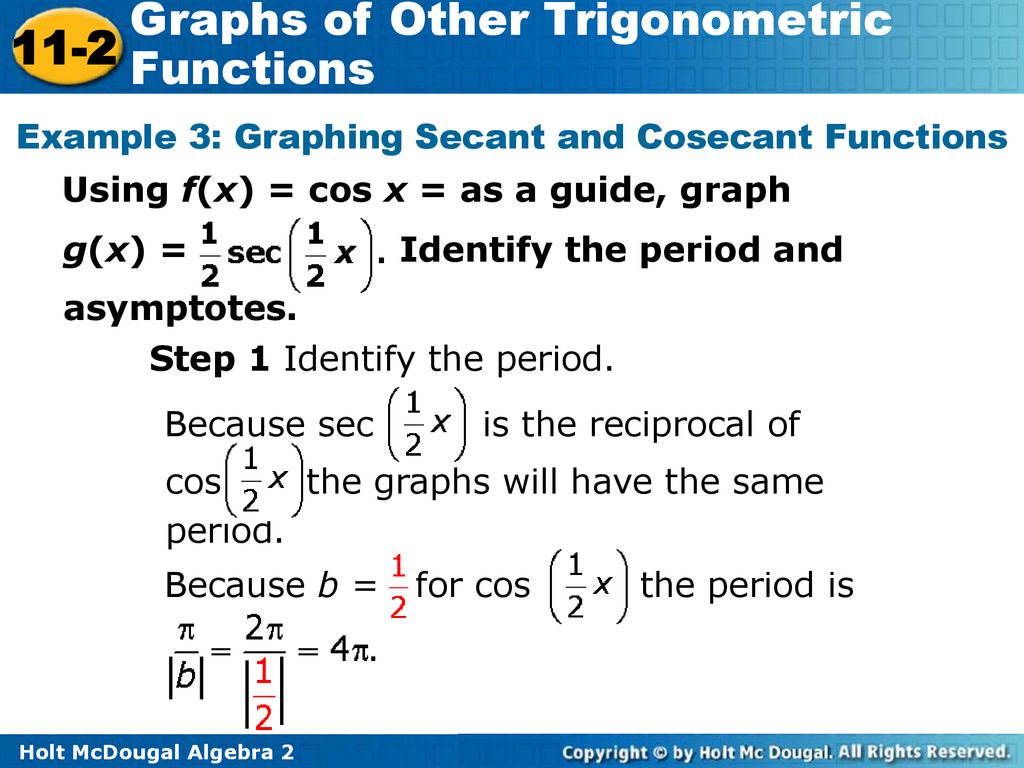



Graphs Of Other Trigonometric Functions Ppt Download
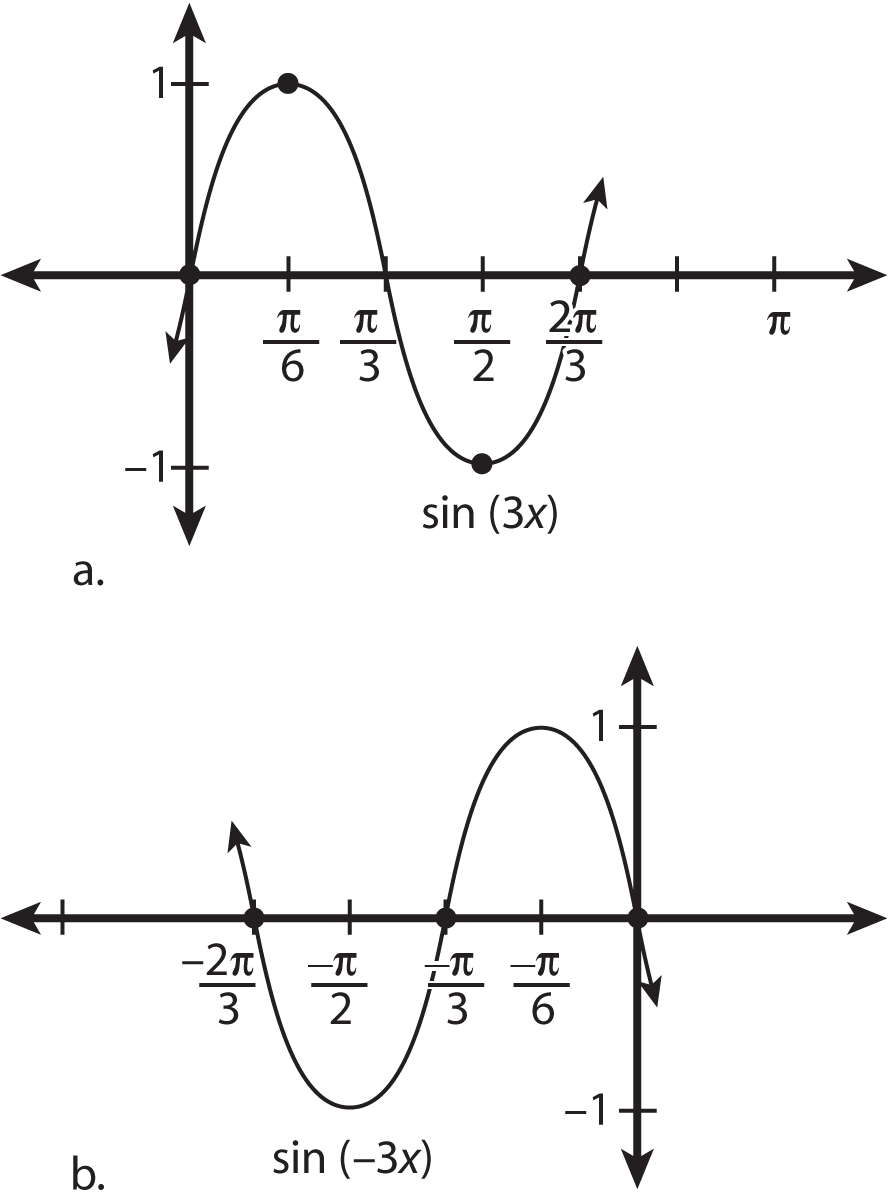



How To Change The Period Of A Sine Or Cosine Graph Dummies




Derivatives Of Trig Functions



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




Question Video Finding The Intervals Of Increasing And Decreasing Of A Function Involving A Trigonometric Function Nagwa




Identify The Correct Statement The Period Of F X Sin Cos X 2 Cos Sinx Is 2pi Youtube




Secant Calculator
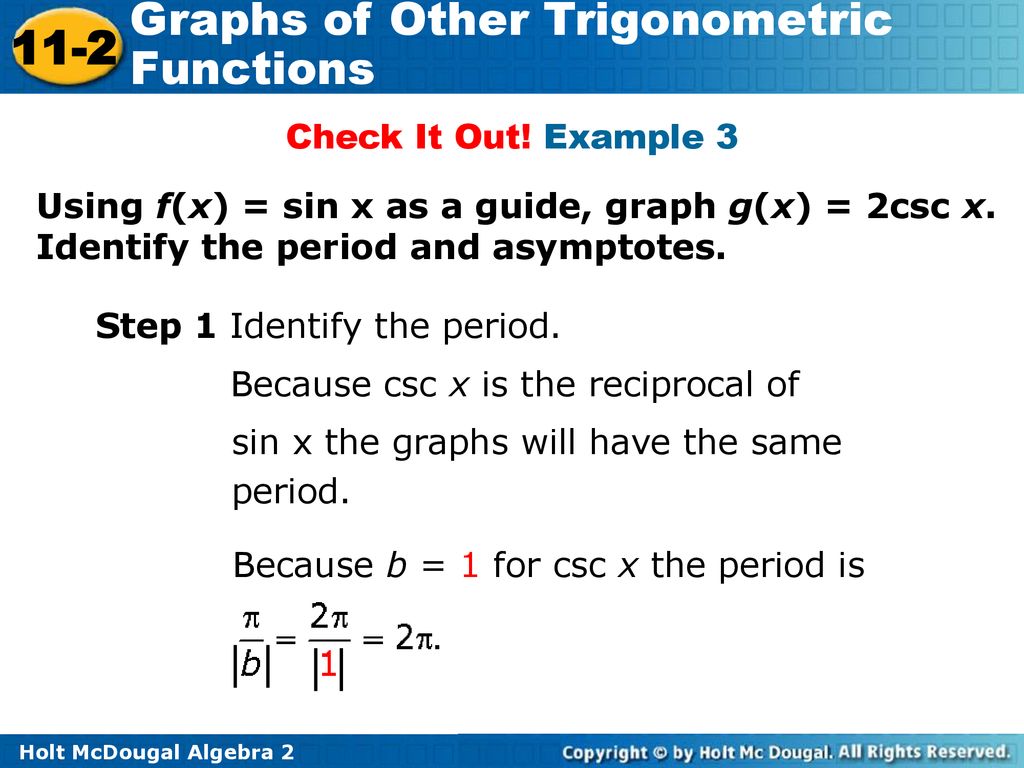



Graphs Of Other Trigonometric Functions Ppt Download




Power Reducing Formulas And How To Use Them With Examples Owlcation



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿